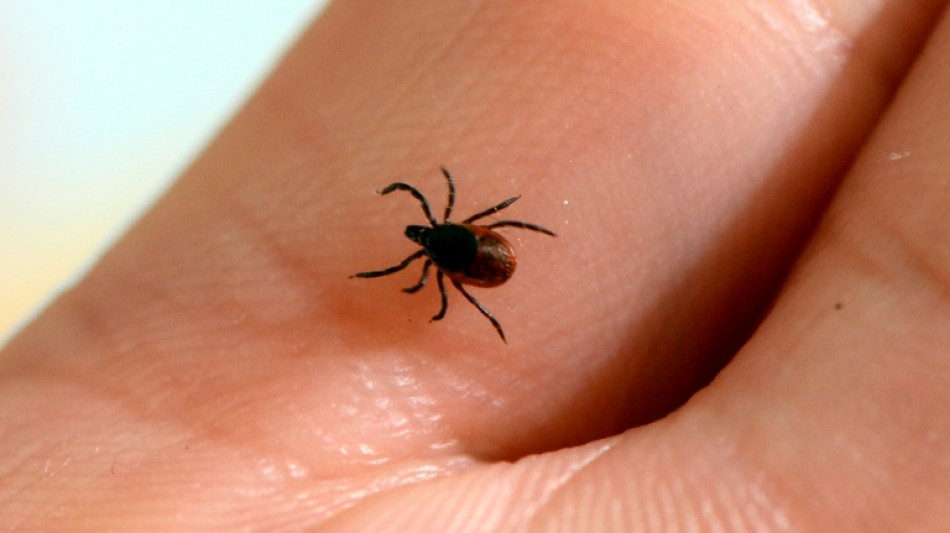
Over 14% of world has had Lyme disease: study

More than 14 percent of the world's population has had Lyme disease, the most common tick-borne illness, according to a major review of the available research published on Tuesday.
Central Europe had the highest rate of infection with 20 percent, while men over the age of 50 living in rural areas were most at risk, the study in the journal BMJ Global Health found.
The condition is rarely fatal, but people bitten by an infected tick often get a rash and suffer flu-like symptoms including muscle and joint ache, headache, nausea and vomiting.
To find out how common Lyme disease is across the world, the researchers pooled data from 89 studies.
The bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi (Bb), which causes the disease, was found in the blood of 14.5 percent of the nearly 160,000 total participants.
"This is the most comprehensive and up-to-date systematic review of the worldwide" prevalence of the disease, the researchers said.
After Central Europe, the regions with the highest antibody rates were Eastern Asia with 15.9 percent, Western Europe with 13.5 percent and Eastern Europe with 10.4 percent.
The Caribbean meanwhile had the lowest rate, with just two percent.
Previous research has shown that the prevalence of tick-borne diseases has doubled in the last 12 years.
Reasons for the rise included longer, drier summers due to climate change, animal migration, habitat loss and "increasingly frequent pet contact", the study said.
Farmers and workers who regularly interact with host animals like dogs and sheep were most at risk of getting bitten by an infected tick, the study found.
It warned that the data could be skewed in regions where Lyme disease is endemic, because health workers are more likely to carry out regular antibody tests there compared to regions where it is less common.
The study also said that research using an analytic technique called western blotting was more reliable and that its use "could significantly improve the accuracy" of future studies.
(O.Tatarinov--DTZ)