Back on the menu? Europeans once ate seaweed, research shows

Europeans now rarely eat seaweed, but it was an important part of their diet until the late Middle Ages, archaeologists said Tuesday, calling for the eco-friendly aquatic plant to be put back on the menu.
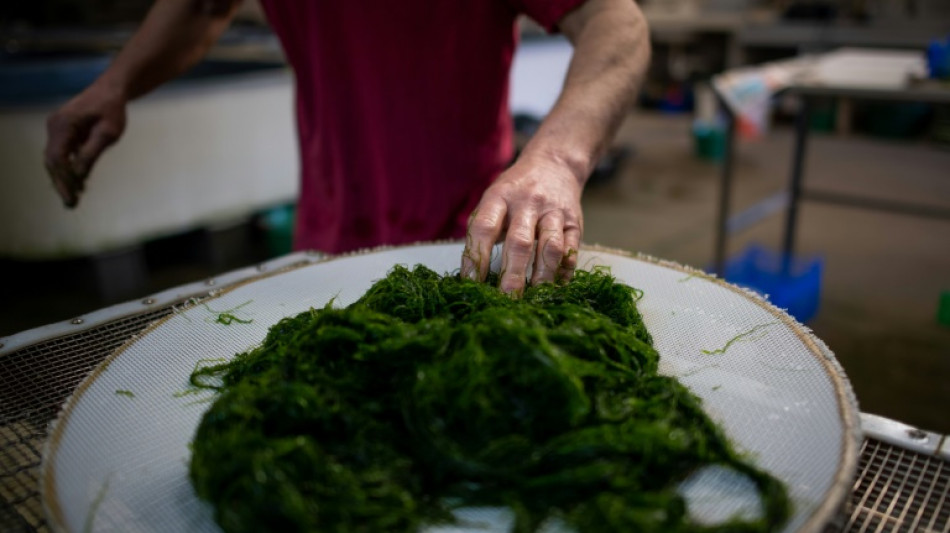
Seaweed, a healthy and sustainable source of protein, is a staple food in some Asian countries such as Japan. But it has long been shunned by traditional Western diets -- with a few exceptions, such as the Welsh dish laverbread.
It was previously thought that since the rise of farming, Europeans had mostly used seaweed as fuel, fertiliser or to feed livestock. It was only eaten to stave off hunger during famine, so the thinking went.
But a new study published in the journal Nature Communications found that Europeans were gobbling up seaweed millennia after that point, and suggested the continent re-embrace the nutritious food.
To find out about ancient seaweed consumption, a UK-led team of researchers analysed dental plaque extracted from the teeth of 74 different people who lived thousands of years ago at 28 sites ranging from Scotland to Spain.
Using a mass spectrometry technique to identify organic compounds, they found evidence that the teeth had chowed down on several different aquatic plants.
Red seaweed was eaten both in Scotland's northern Orkney islands around 5,000 years ago and at Casa Corona in southern Spain 8,000 years ago, the study found.
Freshwater aquatic plants, such as the pondweed Potamogeton, were commonly eaten in Portugal, Scotland and Lithuania, it added.
Karen Hardy, an archaeologist at Scotland's University of Glasgow and the study's lead author, told AFP that aquatic plants were "very likely eaten over a much more wide timescale than we found".
Europeans were previously believed to have turned their noses up at seaweed following the introduction of agriculture more than 10,000 years ago.
However, research in this field has focused on agricultural production, so may have missed out on seaweed, which is easy to find and eat.
The authors of the study said seaweed has the potential to be a locally sourced, low-emission option that does not require the mass farming of the meals normally seen on Europe's plates.
"It's very healthy, it's nutritious, it's available, it's renewable," Hardy said.
"People ate it in the past in Europe," she said, adding hopefully that maybe they will again.
(V.Sørensen--DTZ)